Awesome Curriculum Learning
Some bravo or inspiring research works on the topic of curriculum learning.
A curated list of awesome Curriculum Learning resources. Inspired by awesome-deep-vision, awesome-adversarial-machine-learning, awesome-deep-learning-papers, and awesome-architecture-search
Why Curriculum Learning?
Self-Supervised Learning has become an exciting direction in AI community.
- Bengio: "..." (ICML 2009)
Biological inspired learning scheme.
- Learn the concepts by increasing complexity, in order to allow learner to exploit previously learned concepts and thus ease the abstraction of new ones.
Contributing
Please help contribute this list by contacting me or add pull request
Markdown format:
- Paper Name.
[[pdf]](link)
[[code]](link)
- Key Contribution(s)
- Author 1, Author 2, and Author 3. *Conference Year*
Table of Contents
Mainstreams of curriculum learning
| Tag | Det |
Seg |
Cls |
Trans |
Gen |
Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Detection | Semantic | Image Classification | Transfer Learning | Generation | other types |
| Issues (e.g.,) | long-tail | imbalance | imbalance, noise | long-tail, domain-shift | collapose | - |
SURVEY
- Curriculum Learning: A Survey. [pdf]
- Soviany, Petru and Ionescu, Radu Tudor and Rota, Paolo and Sebe, Nicu. arxiv 2101.10382
2009
- Curriculum Learning. [pdf]
- "Rank the weights of the training examples, and use the rank to guide the order of presentation of examples to the learner."
- Bengio, Yoshua and Louradour, J{'e}r{^o}me and Collobert, Ronan and Weston, Jason. ICML 2009
2015
- Curriculum Learning. [pdf]
- Jiang, Lu and Meng, Deyu and Zhao, Qian and Shan, Shiguang and Hauptmann, Alexander G. AAAI 2015
2017
-
Self-Paced Learning: An Implicit Regularization Perspective. [pdf]
- Fan, Yanbo and He, Ran and Liang, Jian and Hu, Bao-Gang. AAAI 2017
-
Curriculum Dropout. [pdf] [code]
- Morerio, Pietro and Cavazza, Jacopo and Volpi, Riccardo and Vidal, Ren'e and Murino, Vittorio. ICCV 2017
-
Curriculum Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes. [pdf] [code]
- Zhang, Yang and David, Philip and Gong, Boqing. ICCV 2017
2018
-
Curriculum Learning by Transfer Learning: Theory and Experiments with Deep Networks. [pdf]
- "Sort the training examples based on the performance of a pre-trained network on a larger dataset, and then finetune the model to the dataset at hand."
- Weinshall, Daphna and Cohen, Gad and Amir, Dan. ICML 2018
-
Self-Paced Deep Learning for Weakly Supervised Object Detection. [pdf]
- Sangineto, Enver and Nabi, Moin and Culibrk, Dubravko and Sebe, Nicu. TPAMI 2018
-
MentorNet: Learning Data-Driven Curriculum for Very Deep Neural Networks. [pdf] [code]
- Jiang, Lu and Zhou, Zhengyuan and Leung, Thomas and Li, Li-Jia and Li, Fei-Fei. ICML 2018
-
CurriculumNet: Weakly Supervised Learning from Large-Scale Web Images. [pdf] [code]
- Guo, Sheng and Huang, Weilin and Zhang, Haozhi and Zhuang, Chenfan and Dong, Dengke and Scott, Matthew and Huang, Dinglong. ECCV 2018
-
Unsupervised Feature Selection by Self-Paced Learning Regularization. [pdf]
- Zheng, Wei and Zhu, Xiaofeng and Wen, Guoqiu and Zhu, Yonghua and Yu, Hao and Gan, Jiangzhang. Pattern Recognition Letters 2018
-
Learning to Teach with Dynamic Loss Functions. [pdf]
- "A good teacher not only provides his/her students with qualified teaching materials (e.g., textbooks), but also sets up appropriate learning objectives (e.g., course projects and exams) considering different situations of a student."
- Wu, Lijun Wu and Tian, Fei Tian and Xia, Yingce and Fan, Yang Fan and Qin, Tao and Lai, Jianhuang and Liu, Tie-Yan. NeurIPS 2018
-
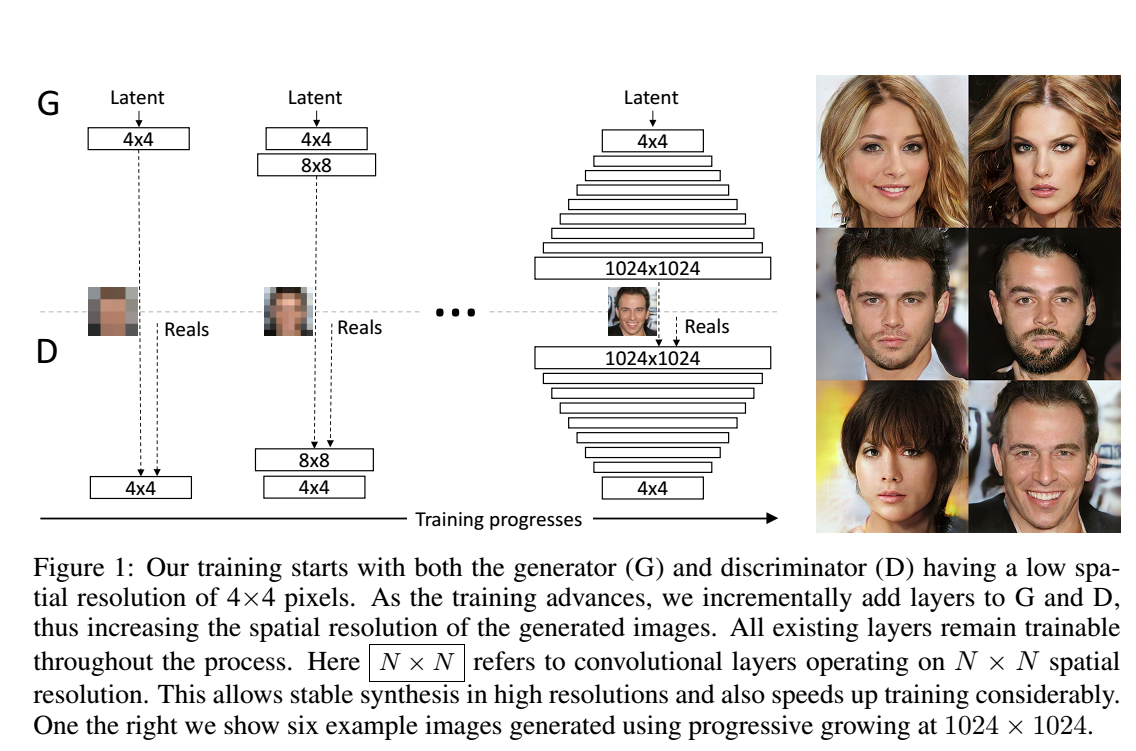
Progressive Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Stability, and Variation.
Gen[pdf] [code]- "The key idea is to grow both the generator and discriminator progressively: starting from a low resolution, we add new layers that model increasingly fine details as training progresses. This both speeds the training up and greatly stabilizes it, allowing us to produce images of unprecedented quality."
- Karras, Tero and Aila, Timo and Laine, Samuli and Lehtinen, Jaakko. ICLR 2018
2019
-
Transferable Curriculum for Weakly-Supervised Domain Adaptation. [pdf] [code]
- Shu, Yang and Cao, Zhangjie and Long, Mingsheng and Wang, Jianmin. AAAI 2019
-
Dynamic Curriculum Learning for Imbalanced Data Classification. [pdf][simple demo]
- Wang, Yiru and Gan, Weihao and Wu, Wei and Yan, Junjie. ICCV 2019
-
Guided Curriculum Model Adaptation and Uncertainty-Aware Evaluation for Semantic Nighttime Image Segmentation. [pdf]
- Sakaridis, Christos and Dai, Dengxin and Gool Van Luc. ICCV 2019
-
On The Power of Curriculum Learning in Training Deep Networks. [pdf]
- Hacohen, Guy and Weinshall, Daphna. ICML 2019
-
Balanced Self-Paced Learning for Generative Adversarial Clustering Network. [pdf]
- Ghasedi, Kamran and Wang, Xiaoqian and Deng, Cheng and Huang, Heng. CVPR 2019
2020
- Breaking the Curse of Space Explosion: Towards Effcient NAS with Curriculum Search. [pdf] [code]
- Guo, Yong and Chen, Yaofo and Zheng, Yin and Zhao, Peilin and Chen, Jian and Huang, Junzhou and Tan, Mingkui. ICML 20
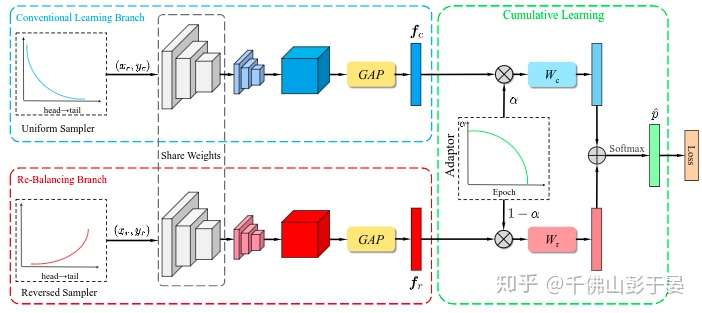
- BBN: Bilateral-Branch Network with Cumulative Learning for Long-Tailed Visual Recognition. [pdf] [code]
- Zhou, Boyan and Cui, Quan and Wei, Xiu-Shen and Chen, Zhao-Min. CVPR 2020
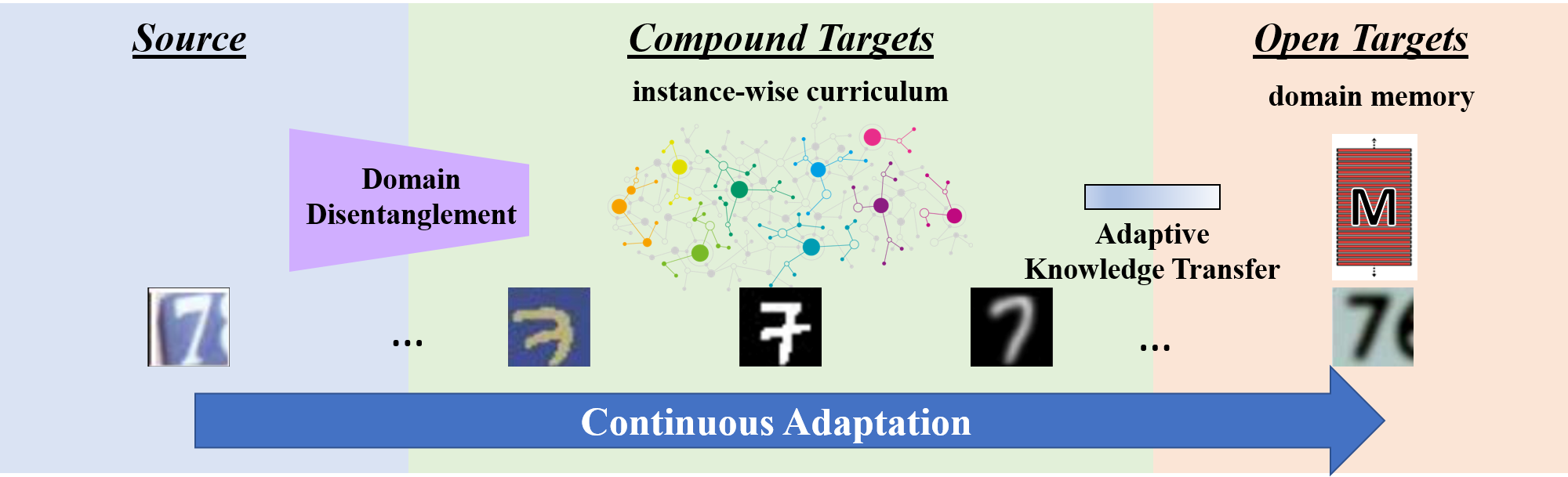
- Open Compound Domain Adaptation. [pdf] [code]
- Liu, Ziwei and Miao, Zhongqi and Pan, Xingang and Zhan, Xiaohang and Lin, Dahua and Yu, Stella X and Gong, Boqing. CVPR 2020
-
Curriculum Manager for Source Selection in Multi-Source Domain Adaptation. [pdf][code]
- Yang, Luyu and Balaji, Yogesh and Lim, Ser-Nam and Shrivastava, Abhinav. ECCV 2020
-
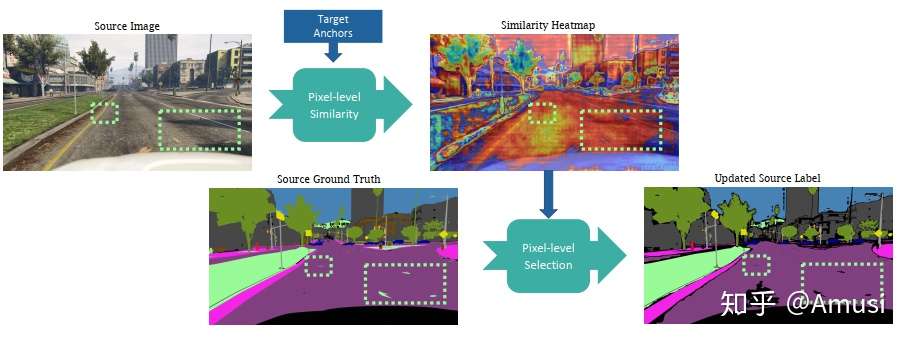
Content-Consistent Matching for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation.
Seg[pdf] [code]- "to acquire those synthetic images that share similar distribution with the real ones in the target domain, so that the domain gap can be naturally alleviated by employing the content-consistent synthetic images for training."
- "not all the source images could contribute to the improvement of adaptation performance, especially at certain training stages."
- Li, Guangrui and Kang, Guokiang and Liu, Wu and Wei, Yunchao and Yang, Yi . ECCV 2020
-
DA-NAS: Data Adapted Pruning for Efficient Neural Architecture Search. [pdf]
- "Our method is based on an interesting observation that the learning speed for blocks in deep neural networks is related to the difficulty of recognizing distinct categories. We carefully design a progressive data adapted pruning strategy for efficient architecture search. It will quickly trim low performed blocks on a subset of target dataset (e.g., easy classes), and then gradually find the best blocks on the whole target dataset."
- Dai, Xiyang and Chen, Dongdong and Liu, Mengchen and Chen, Yinpeng and Yuan, Lu. ECCV 2020
-
Label-similarity Curriculum Learning. [pdf] [code]
- "The idea is to use a probability distribution over classes as target label, where the class probabilities reflect the similarity to the true class. Gradually, this label representation is shifted towards the standard one-hot-encoding."
- Dogan, Urun and Deshmukh, A. Aniket, and Machura, Marcin and Igel, Christian. ECCV 2020
-
Self-paced Contrastive Learning with Hybrid Memory for Domain Adaptive Object Re-ID. [pdf] [code] [zhihu]
- Ge, Yixiao and Zhu, Feng and Chen, Dapeng and Zhao, Rui and Li, Hongsheng. NeurIPS 2020
-
Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation via Dynamic Self-Training and Class-Balanced Curriculum. [pdf] [code]
- Feng, Zhengyang and Zhou, Qianyu and Cheng, Guangliang and Tan, Xin and Shi, Jianping and Ma, Lizhuang. arXiv 2004.08514
-
Evolutionary Population Curriculum for Scaling Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. [pdf][code]
- "Evolutionary Population Curriculum (EPC), a curriculum learning paradigm that scales up MultiAgent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) by progressively increasing the population of training agents in a stage-wise manner."
- Long, Qian and Zhou, Zihan and Gupta, Abhibav and Fang, Fei and Wu, Yi and Wang, Xiaolong. ICLR 2020
-
Self-Paced Deep Reinforcement Learning. [pdf]
- Klink, Pascal and D'Eramo, Carlo and Peters, R. Jan and Pajarinen, Joni. NeurIPS 2020
-
Automatic Curriculum Learning through Value Disagreement. [pdf]
- " When biological agents learn, there is often an organized and meaningful order to which learning happens."
- "Our key insight is that if we can sample goals at the frontier of the set of goals that an agent is able to reach, it will provide a significantly stronger learning signal compared to randomly sampled goals"
- Zhang, Yunzhi and Abbeel, Pieter and Pinto, Lerrel. NeurIPS 2020
-
Curriculum by Smoothing. [pdf] [code]
- Sinha Samarth and Garg Animesh and Larochelle Hugo. NeurIPS 2020
-
Curriculum Learning by Dynamic Instance Hardness. [pdf]
- Zhou, Tianyi and Wang, Shengjie and Bilmes, A. Jeff. NeurIPS 2020
2021
-
Robust Curriculum Learning: from clean label detection to noisy label self-correction. [pdf] [online review]
- "Robust curriculum learning (RoCL) improves noisy label learning by periodical transitions from supervised learning of clean labeled data to self-supervision of wrongly-labeled data, where the data are selected according to training dynamics."
- Zhou, Tianyi and Wang, Shengjie and Bilmes, Jeff. ICLR 2021
-
Robust Early-Learning: Hindering The Memorization of Noisy Labels. [pdf] [online review]
- "Robust early-learning: to reduce the side effect of noisy labels before early stopping and thus enhance the memorization of clean labels. Specifically, in each iteration, we divide all parameters into the critical and non-critical ones, and then perform different update rules for different types of parameters."
- Xia, Xiaobo and Liu, Tongliang and Han, Bo and Gong, Chen and Wang, Nannan and Ge, Zongyuan and Chang, Yi. ICLR 2021
-
When Do Curricula Work? [pdf]
- "We find that for standard benchmark datasets, curricula have only marginal benefits, and that randomly ordered samples perform as well or better than curricula and anti-curricula, suggesting that any benefit is entirely due to the dynamic training set size. ... Our experiments demonstrate that curriculum, but not anti-curriculum or random ordering can indeed improve the performance either with limited training time budget or in the existence of noisy data."
- Wu, Xiaoxia and Dyer, Ethan and Neyshabur, Behnam. ICLR 2021 (oral)
-
Curriculum Graph Co-Teaching for Multi-Target Domain Adaptation. [pdf] [code]
- Roy, Subhankar and Krivosheev, Evgeny and Zhong, Zhun and Sebe, Nicu and Ricci, Elisa. CVPR 2021
- TeachMyAgent: a Benchmark for Automatic Curriculum Learning in Deep RL. [pdf] [code]
- Romac, Clément and Portelas, Rémy and Hofmann, Katja and Oudeyer, Pierre-Yves. ICML 2021
-
Self-Paced Context Evaluation for Contextual Reinforcement Learning. [pdf]
- "To improve sample efficiency for learning on such instances of a problem domain, we present Self-Paced Context Evaluation (SPaCE). Based on self-paced learning, \spc automatically generates \task curricula online with little computational overhead. To this end, SPaCE leverages information contained in state values during training to accelerate and improve training performance as well as generalization capabilities to new instances from the same problem domain."
- Eimer, Theresa and Biedenkapp, André and Hutter, Frank and Lindauer Marius. ICML 2021
-
Curriculum Learning by Optimizing Learning Dynamics. [pdf] [code]
- Zhou, Tianyi and Wang, Shengjie and Bilmes, Jeff. AISTATS 2021