Project 3: Collaboration and Competition
Project Details
For this project, you will work with the Tennis environment.
In this environment, two agents control rackets to bounce a ball over a net. If an agent hits the ball over the net, it receives a reward of +0.1. If an agent lets a ball hit the ground or hits the ball out of bounds, it receives a reward of -0.01. Thus, the goal of each agent is to keep the ball in play.
The observation space consists of 8 variables corresponding to the position and velocity of the ball and racket. Each agent receives its own, local observation. Two continuous actions are available, corresponding to movement toward (or away from) the net, and jumping.
The task is episodic, and in order to solve the environment, your agents must get an average score of +0.5 (over 100 consecutive episodes, after taking the maximum over both agents). Specifically,
- After each episode, we add up the rewards that each agent received (without discounting), to get a score for each agent. This yields 2 (potentially different) scores. We then take the maximum of these 2 scores.
- This yields a single score for each episode.
The environment is considered solved, when the average (over 100 episodes) of those scores is at least +0.5.
Getting Started
Dependencies
To set up your python environment to run the code in the notebook, follow the instructions below.
-
Create (and activate) a new environment with Python 3.6.
- Linux or Mac:
conda create --name drlnd python=3.6 source activate drlnd- Windows:
conda create --name drlnd python=3.6 activate drlnd
-
Clone the repository, and navigate to the
python/folder. Then, install several dependencies.
git clone https://github.com/udacity/deep-reinforcement-learning.git
cd deep-reinforcement-learning/python
pip install .
Note: You may encounter issues with installing Pytorch 0.4.0. In that case, please replace the file python/requirements.txt with the file requirements.txt inside this project.
- Create an IPython kernel for the
drlndenvironment.
python -m ipykernel install --user --name drlnd --display-name "drlnd"
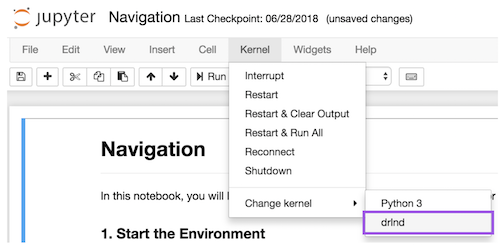
- Before running code in a notebook, change the kernel to match the
drlndenvironment by using the drop-downKernelmenu.
Instructions
-
Download the environment from one of the links below. You need only select the environment that matches your operating system:
- Linux: click here
- Mac OSX: click here
- Windows (32-bit): click here
- Windows (64-bit): click here
(For Windows users) Check out this link if you need help with determining if your computer is running a 32-bit version or 64-bit version of the Windows operating system.
(For AWS) If you'd like to train the agent on AWS (and have not enabled a virtual screen), then please use this link to obtain the "headless" version of the environment. You will not be able to watch the agent without enabling a virtual screen, but you will be able to train the agent. (To watch the agent, you should follow the instructions to enable a virtual screen, and then download the environment for the Linux operating system above.)
-
Place the extracted files in the same folder as the notebook
Tennis.ipynb. -
Load the notebook with Jupyter notebook. (The command to start Jupyter notebook is
jupyter notebook) -
Follow further instructions in the notebook.