pm-prophet
Pymc3-based universal time series prediction and decomposition library (inspired by Facebook Prophet). However, while Faceook prophet is a well-defined model, pm-prophet allows for total flexibility in the choice of priors and thus is potentially suited for a wider class of estimation problems.
Table of Contents
Installing pm-prophet
PM-Prophet installation is straightforward using pip: pip install pmprophet
Note that the key dependency of pm-prophet is PyMc3 a library that depends on Theano.
Key Features
- Nowcasting & Forecasting
- Intercept, growth
- Regressors
- Holidays
- Additive & multiplicative seasonality
- Fitting and plotting
- Custom choice of priors (not in Facebook's prophet original model)
- Changepoints in growth
- Automatic changepoint location detection (not in Facebook's prophet original model)
- Fitting with NUTS/AVDI/Metropolis
Experimental warning
⚠️
- Note that automatic changepoint detection is experimental
Differences with Prophet:
- Saturating growth is not implemented
- Uncertainty estimation is different
- All components (including seasonality) need to be explicitly added to the model
- By design pm-prophet places a big emphasis on posteriors and uncertainty estimates, and therefore it won't use MAP for it's estimates.
- While Faceook prophet is a well-defined fixed model, pm-prophet allows for total flexibility in the choice of priors and thus is potentially suited for a wider class of estimation problems
Peyton Manning example
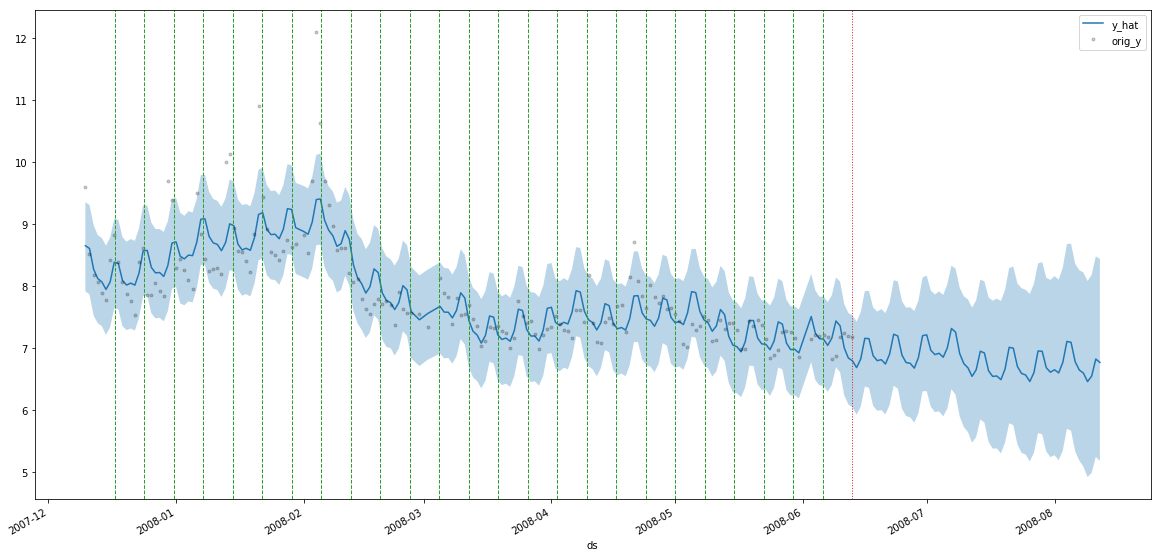
Predicting the Peyton Manning timeseries:
import pandas as pd
from pmprophet.model import PMProphet, Sampler
df = pd.read_csv("examples/example_wp_log_peyton_manning.csv")
df = df.head(180)
# Fit both growth and intercept
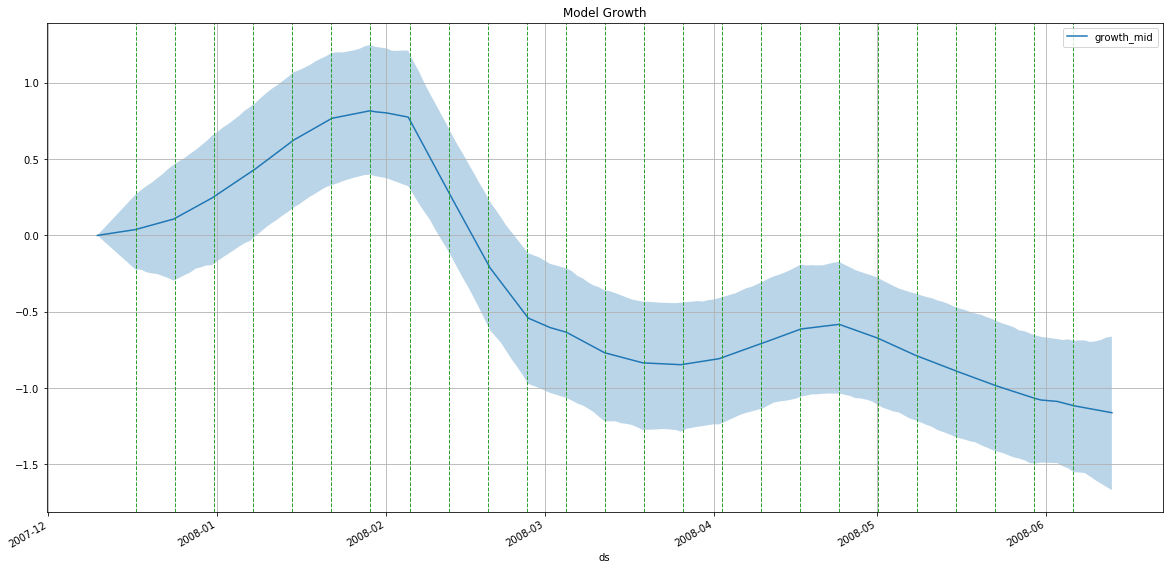
m = PMProphet(df, growth=True, intercept=True, n_changepoints=25, changepoints_prior_scale=.01, name='model')
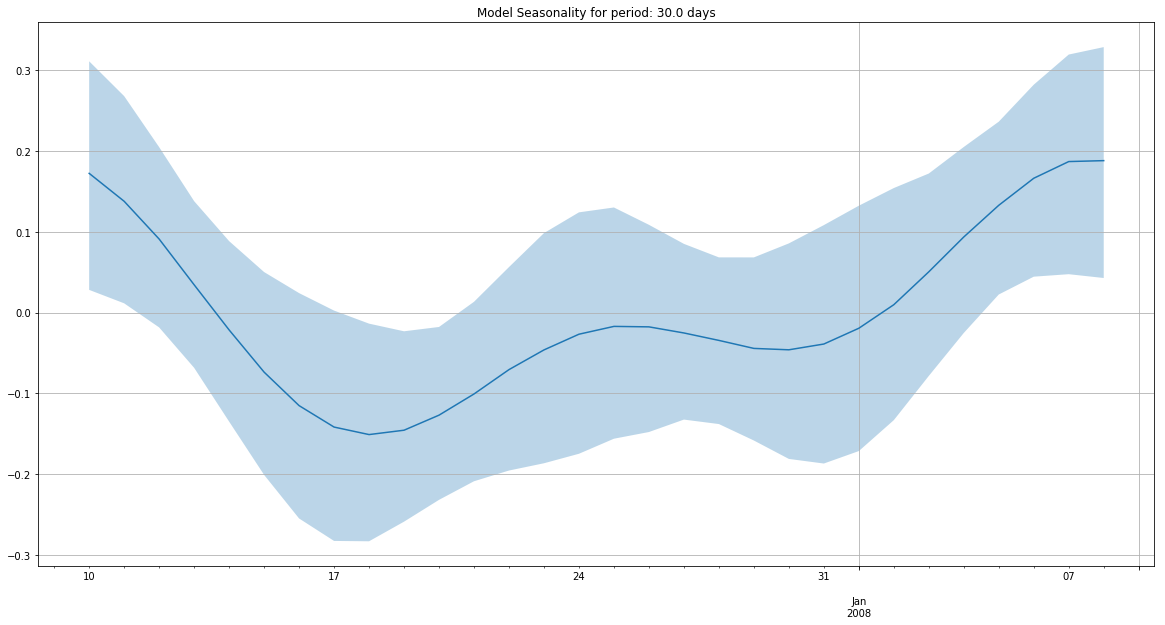
# Add monthly seasonality (order: 3)
m.add_seasonality(seasonality=30, fourier_order=3)
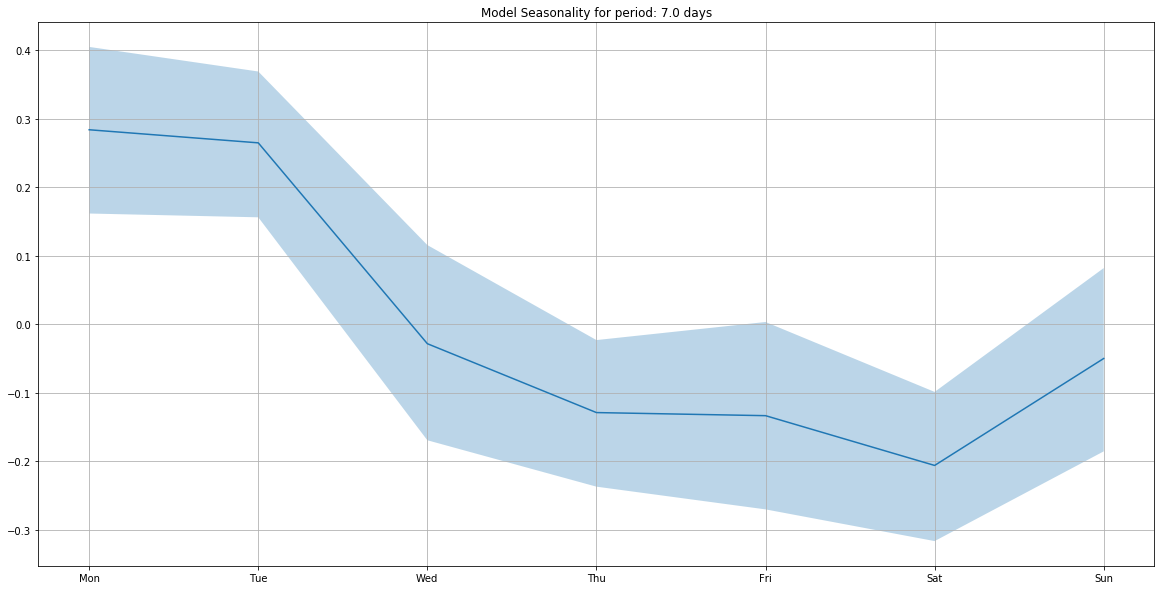
# Add weekly seasonality (order: 3)
m.add_seasonality(seasonality=7, fourier_order=3)
# Fit the model (using NUTS)
m.fit(method=Sampler.NUTS)
ddf = m.predict(60, alpha=0.2, include_history=True, plot=True)
m.plot_components(
intercept=False,
)
Custom Priors
One of the main reason why PMProphet was built is to allow custom priors for the modeling.
The default priors are:
| Variable | Prior | Parameters |
|---|---|---|
regressors |
Laplace | loc:0, scale:2.5 |
holidays |
Laplace | loc:0, scale:2.5 |
seasonality |
Laplace | loc:0, scale:0.05 |
growth |
Laplace | loc:0, scale:10 |
changepoints |
Laplace | loc:0, scale:2.5 |
intercept |
Normal | loc:y.mean, scale: 2 * y.std |
sigma |
Half Cauchy | tau:10 |
But you can change model priors by inspecting and modifying the distributions stored in
m.priors
which is a dictionary of {prior: pymc3-distribution}.
In the example below we will model an additive time-series by imposing a "positive coefficients" constraint by using an Exponential distribution instead of a Laplacian distribution for the regressors.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import pymc3 as pm
from pmprophet.model import PMProphet, Sampler
n_timesteps = 100
n_regressors = 20
regressors = np.random.normal(size=(n_timesteps, n_regressors))
coeffs = np.random.exponential(size=n_regressors) + np.random.normal(size=n_regressors)
# Note that min(coeffs) could be negative due to the white noise
regressors_names = [str(i) for i in range(n_regressors)]
df = pd.DataFrame()
df['y'] = np.dot(regressors, coeffs)
df['ds'] = pd.date_range('2017-01-01', periods=n_timesteps)
for idx, regressor in enumerate(regressors_names):
df[regressor] = regressors[:, idx]
m = PMProphet(df, growth=False, intercept=False, n_changepoints=0, name='model')
with m.model:
# Remember to suffix _<model-name> to the custom priors
m.priors['regressors'] = pm.Exponential('regressors_%s' % m.name, 1, shape=n_regressors)
for regressor in regressors_names:
m.add_regressor(regressor)
m.fit(
draws=10 ** 4,
method=Sampler.NUTS,
)
m.plot_components()
Automatic changepoint detection (
⚠️
experimental)
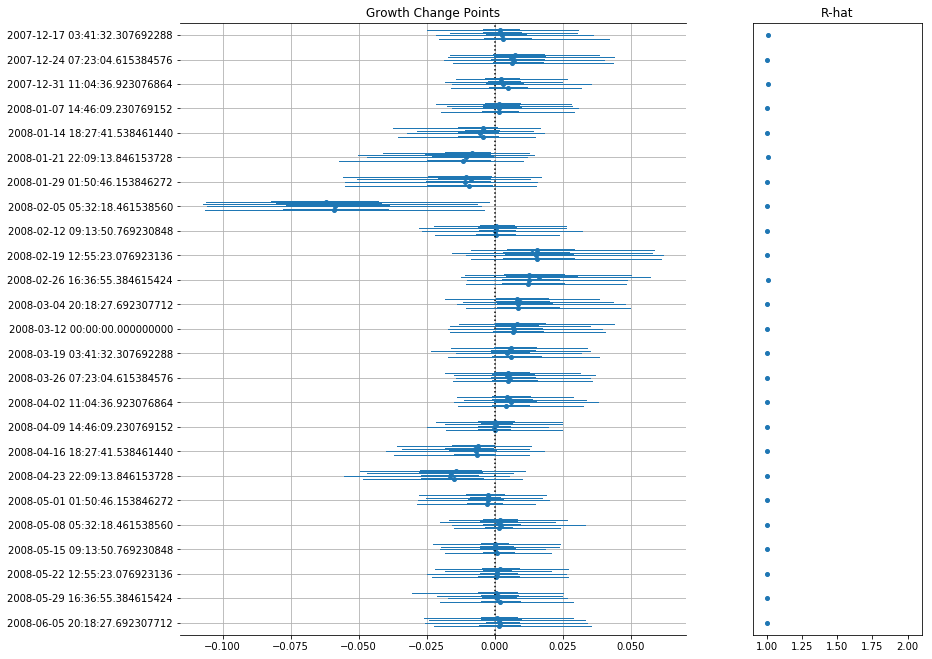
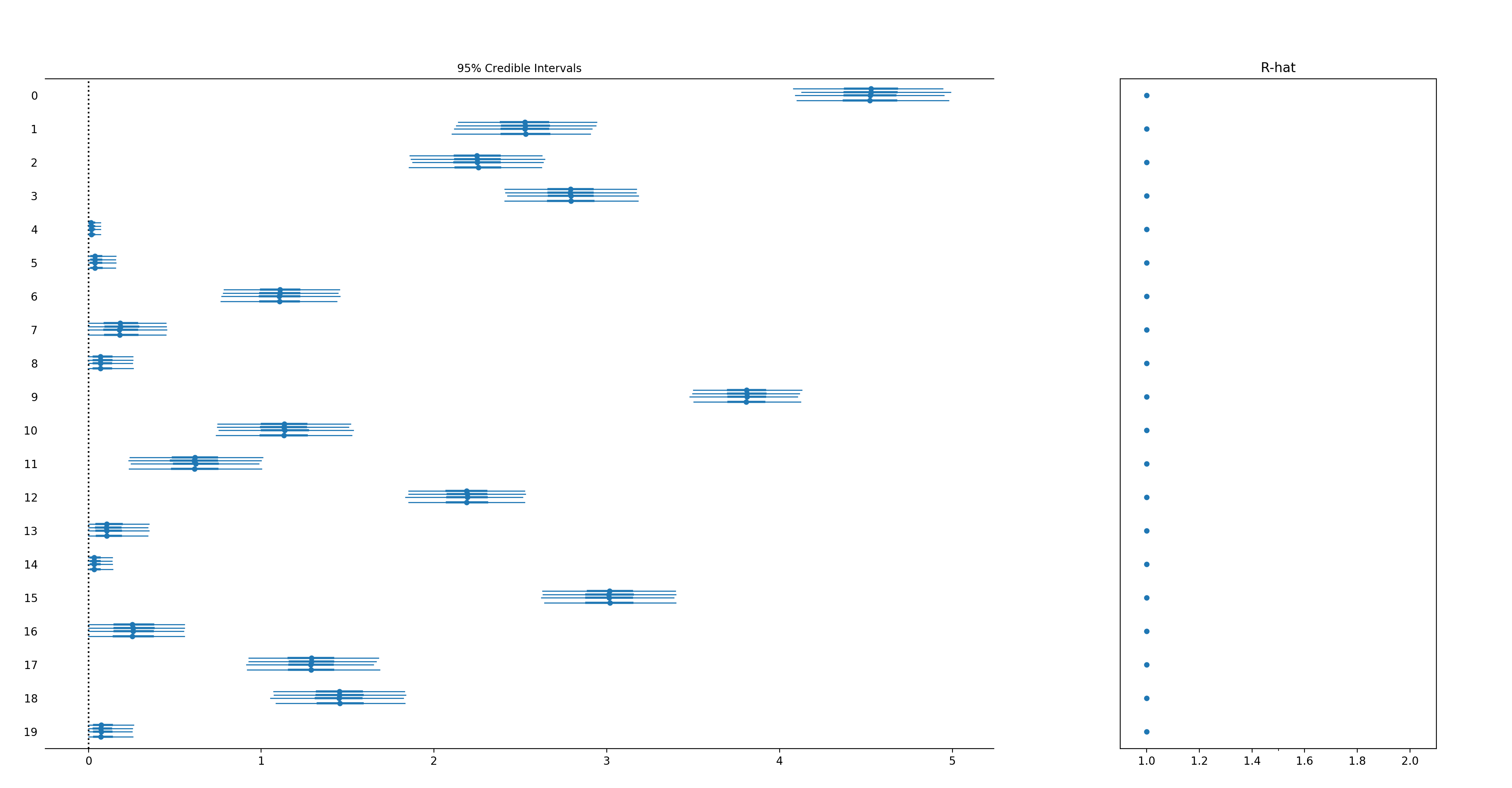
Pm-prophet is equipped with a non-parametric truncated Dirichlet Process allowing it to automatically detect changepoints in the trend.
To enable it simply initialize the model with auto_changepoints=True as follows:
from pmprophet.model import PMProphet, Sampler
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv("examples/example_wp_log_peyton_manning.csv")
df = df.head(180)
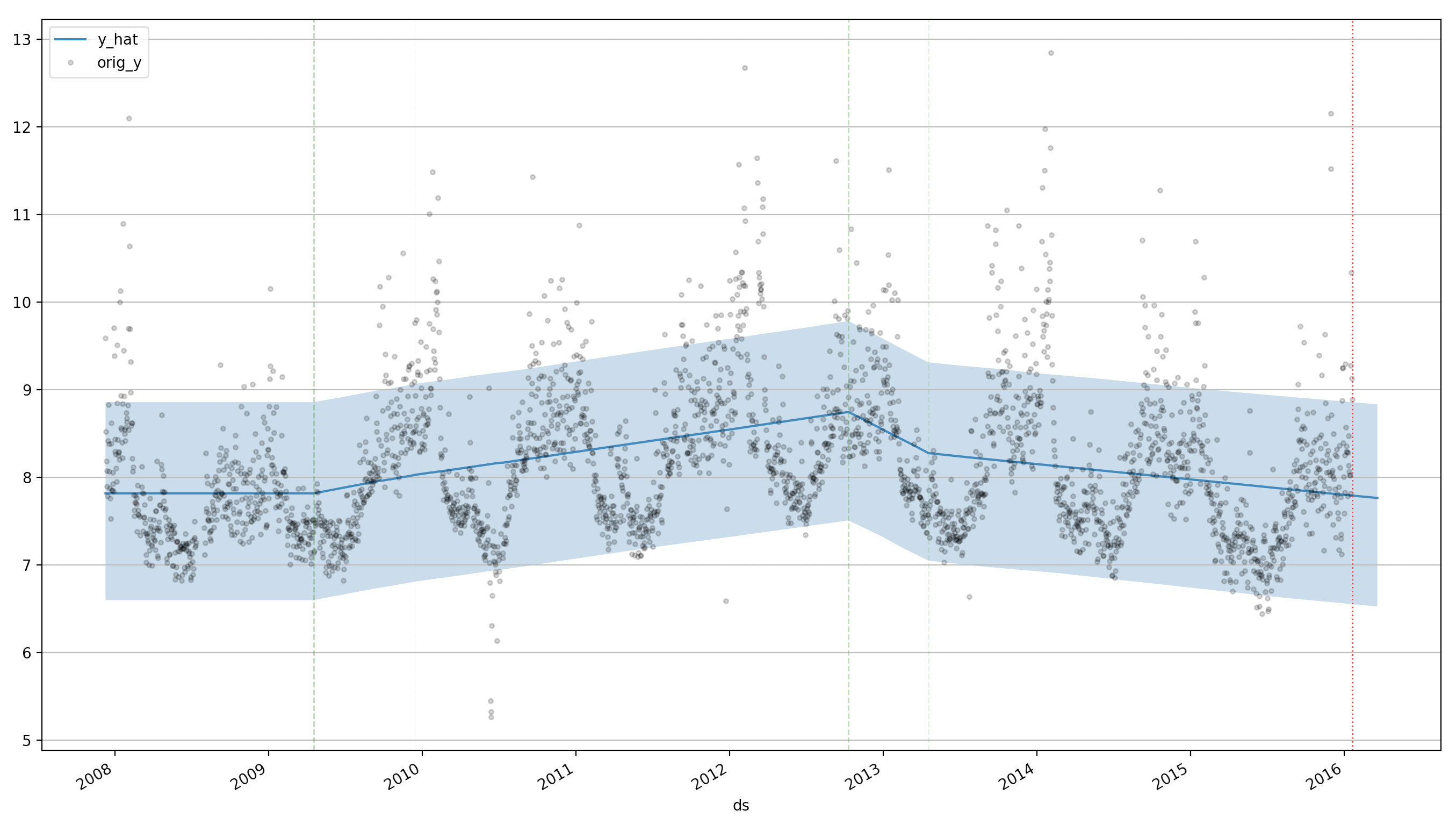
m = PMProphet(df, auto_changepoints=True, growth=True, intercept=True, name='model')
m.fit(method=Sampler.METROPOLIS, draws=2000)
m.predict(60, alpha=0.2, include_history=True, plot=True)
m.plot_components(
intercept=False,
)
Where n_changepoints is interpreted as the truncation point for the Dirichlet Process.
Pm-prophet will then decide which changepoint values make sense and add a custom weight to them. A call to plot_components() will reveal the changepoint map:
A few caveats exist:
- It's slow to fit since it's a non-parametric model
- For best results use NUTS as method
- It will likely require more than the default number of draws to converge