Fill Voids
# PYTHON
import fill_voids
img = ... # 2d or 3d binary image
filled_image = fill_voids.fill(img, in_place=False) # in_place allows editing of original image
filled_image, N = fill_voids.fill(img, return_fill_count=True) # returns number of voxels filled in
// C++ #include "fill_voids.hpp" size_t sx, sy, sz; sx = sy = sz = 512; uint8_t* labels = ...; // 512x512x512 binary image // modifies labels as a side effect, returns number of voxels filled in size_t fill_ct = fill_voids::binary_fill_holes<uint8_t>(labels, sx, sy, sz); // 3D // let labels now represent a 512x512 2D image size_t fill_ct = fill_voids::binary_fill_holes<uint8_t>(labels, sx, sy); // 2D
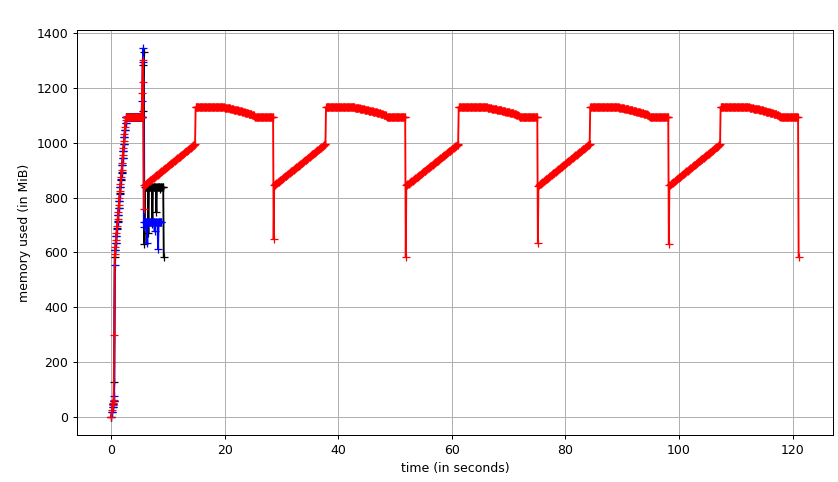
Fig. 1: Filling five labels using SciPy binary_fill_holes vs fill_voids from a 512x512x512 densely labeled connectomics segmentation. (black) fill_voids 1.1.0 (blue) fill_voids 1.1.0 with `in_place=True` (red) scipy 1.4.1. In this test, fill_voids (`in_place=False`) is significantly faster than scipy with lower memory usage.
This library contains both 2D and 3D void filling algorithms, similar in function to scipy.ndimage.morphology.binary_fill_holes, but with an eye towards higher performance. The SciPy hole filling algorithm uses slow serial dilations.
The current version of this library uses a scan line flood fill of the background labels and then labels everything not filled as foreground.
pip Installation
pip install fill-voids
If there's no binary for your platform and you have a C++ compiler try:
sudo apt-get install python3-dev # This is for Ubuntu, but whatever is appropriate for you
pip install numpy
pip install fill-voids --no-binary :all:
Current Algorithm
- Raster scan and mark every foreground voxel
2for pre-existing foreground. - Raster scan each face of the current image and the first time a black pixel (
0) is encountered after either starting or enountering a foreground pixel, add that location to a stack. - Flood fill (six connected) with the visited background color (
1) in sequence from each location in the stack that is not already foreground. - Write out a binary image the same size as the input mapped as buffer != 1 (i.e. 0 or 2). This means non-visited holes and foreground will be marked as
1for foreground and the visited background will be marked as0.
We improve performance significantly by using libdivide to make computing x,y,z coordinates from array index faster, by scanning right and left to take advantage of machine memory speed, by only placing a neighbor on the stack when we've either just started a scan or just passed a foreground pixel while scanning.
Multi-Label Concept
Similarly to the connected-components-3d and euclidean-distance-3d projects, in connectomics, it can be common to want to apply void filling algorithms to all labels within a densely packed volume. A multi-label algorithm can be much faster than even the fastest serial application of a binary algorithm. Here's how this might go given an input image I:
- Compute M = max(I)
- Perform the fill as in the binary algorithm labeling the surrounding void as M+1. This means all voids are now either legitimate and can be filled or holes in-between labels.
- Raster scan through the volume. If a new void is encountered, we must determine if it is fillable or an in-between one which will not be filled.
- On encountering the void, record the last label seen and contour trace around it. If only that label is encountered during contour tracing, it is fillable. If another label is encountered, it is not fillable.
- During the contour trace, mark the trace using an integer not already used, such as M+2. If that label is encountered in the future, you'll know what to fill between it and the next label encountered based on the fillable determination. This phase stops when either the twin of the first M+2 label is encountered or when futher contour tracing isn't possible (in the case of single voxel gaps).
- (Inner Labels) If another label is encountered in the middle of a void, contour trace around it and mark the boundary with the same M+2 label that started the current fill.