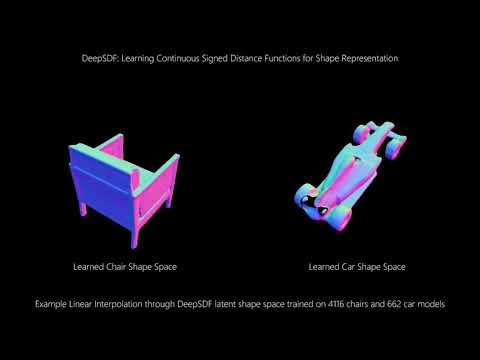
DeepSDF
This is an implementation of the CVPR '19 paper "DeepSDF: Learning Continuous Signed Distance Functions for Shape Representation" by Park et al. See the paper here.
Citing DeepSDF
If you use DeepSDF in your research, please cite the paper:
@InProceedings{Park_2019_CVPR,
author = {Park, Jeong Joon and Florence, Peter and Straub, Julian and Newcombe, Richard and Lovegrove, Steven},
title = {DeepSDF: Learning Continuous Signed Distance Functions for Shape Representation},
booktitle = {The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2019}
}
File Organization
The various Python scripts assume a shared organizational structure such that the output from one script can easily be used as input to another. This is true for both preprocessed data as well as experiments which make use of the datasets.
Data Layout
The DeepSDF code allows for pre-processing of meshes from multiple datasets and stores them in a unified data source. It also allows for separation of meshes according to class at the dataset level. The structure is as follows:
<data_source_name>/
.datasources.json
SdfSamples/
<dataset_name>/
<class_name>/
<instance_name>.npz
SurfaceSamples/
<dataset_name>/
<class_name>/
<instance_name>.ply
Subsets of the unified data source can be reference using split files, which are stored in a simple JSON format. For examples, see examples/splits/.
The file datasources.json stores a mapping from named datasets to paths indicating where the data came from. This file is referenced again during evaluation to compare against ground truth meshes (see below), so if this data is moved this file will need to be updated accordingly.
Experiment Layout
Each DeepSDF experiment is organized in an "experiment directory", which collects all of the data relevant to a particular experiment. The structure is as follows:
<experiment_name>/
specs.json
Logs.pth
LatentCodes/
<Epoch>.pth
ModelParameters/
<Epoch>.pth
OptimizerParameters/
<Epoch>.pth
Reconstructions/
<Epoch>/
Codes/
<MeshId>.pth
Meshes/
<MeshId>.pth
Evaluations/
Chamfer/
<Epoch>.json
EarthMoversDistance/
<Epoch>.json
The only file that is required to begin an experiment is 'specs.json', which sets the parameters, network architecture, and data to be used for the experiment.
How to Use DeepSDF
Pre-processing the Data
In order to use mesh data for training a DeepSDF model, the mesh will need to be pre-processed. This can be done with the preprocess_data.py executable. The preprocessing code is in C++ and has the following requirements:
With these dependencies, the build process follows the standard CMake procedure:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make -j
Once this is done there should be two executables in the DeepSDF/bin directory, one for surface sampling and one for SDF sampling. With the binaries, the dataset can be preprocessed using preprocess_data.py.
Preprocessing with Headless Rendering
The preprocessing script requires an OpenGL context, and to acquire one it will open a (small) window for each shape using Pangolin. If Pangolin has been compiled with EGL support, you can use the "headless" rendering mode to avoid the windows stealing focus. Pangolin's headless mode can be enabled by setting the PANGOLIN_WINDOW_URI environment variable as follows:
export PANGOLIN_WINDOW_URI=headless://
Training a Model
Once data has been preprocessed, models can be trained using:
python train_deep_sdf.py -e <experiment_directory>
Parameters of training are stored in a "specification file" in the experiment directory, which (1) avoids proliferation of command line arguments and (2) allows for easy reproducibility. This specification file includes a reference to the data directory and a split file specifying which subset of the data to use for training.
Visualizing Progress
All intermediate results from training are stored in the experiment directory. To visualize the progress of a model during training, run:
python plot_log.py -e <experiment_directory>
By default, this will plot the loss but other values can be shown using the --type flag.
Continuing from a Saved Optimization State
If training is interrupted, pass the --continue flag along with a epoch index to train_deep_sdf.py to continue from the saved state at that epoch. Note that the saved state needs to be present --- to check which checkpoints are available for a given experiment, check the `ModelParameters', 'OptimizerParameters', and 'LatentCodes' directories (all three are needed).
Reconstructing Meshes
To use a trained model to reconstruct explicit mesh representations of shapes from the test set, run:
python reconstruct.py -e <experiment_directory>
This will use the latest model parameters to reconstruct all the meshes in the split. To specify a particular checkpoint to use for reconstruction, use the --checkpoint flag followed by the epoch number. Generally, test SDF sampling strategy and regularization could affect the quality of the test reconstructions. For example, sampling aggressively near the surface could provide accurate surface details but might leave under-sampled space unconstrained, and using high L2 regularization coefficient could result in perceptually better but quantitatively worse test reconstructions.
Shape Completion
The current release does not include code for shape completion. Please check back later!
Evaluating Reconstructions
Before evaluating a DeepSDF model, a second mesh preprocessing step is required to produce a set of points sampled from the surface of the test meshes. This can be done as with the sdf samples, but passing the --surface flag to the pre-processing script. Once this is done, evaluations are done using:
python evaluate.py -e <experiment_directory> -d <data_directory> --split <split_filename>
Note on Table 3 from the CVPR '19 Paper
Given the stochastic nature of shape reconstruction (shapes are reconstructed via gradient descent with a random initialization), reconstruction accuracy will vary across multiple reruns of the same shape. The metrics listed in Table 3 for the "chair" and "plane" are the result of performing two reconstructions of each shape and keeping the one with the lowest chamfer distance. The code as released does not support this evaluation and thus the reproduced results will likely differ from those produced in the paper. For example, our test run with the provided code produced Chamfer distance (multiplied by 103) mean and median of 0.157 and 0.062 respectively for the "chair" class and 0.101 and 0.044 for the "plane" class (compared to 0.204, 0.072 for chairs and 0.143, 0.036 for planes reported in the paper).
Examples
Here's a list of commands for a typical use case of training and evaluating a DeepSDF model using the "sofa" class of the ShapeNet version 2 dataset.
# navigate to the DeepSdf root directory
cd [...]/DeepSdf
# create a home for the data
mkdir data
# pre-process the sofas training set (SDF samples)
python preprocess_data.py --data_dir data --source [...]/ShapeNetCore.v2/ --name ShapeNetV2 --split examples/splits/sv2_sofas_train.json --skip
# train the model
python train_deep_sdf.py -e examples/sofas
# pre-process the sofa test set (SDF samples)
python preprocess_data.py --data_dir data --source [...]/ShapeNetCore.v2/ --name ShapeNetV2 --split examples/splits/sv2_sofas_test.json --test --skip
# pre-process the sofa test set (surface samples)
python preprocess_data.py --data_dir data --source [...]/ShapeNetCore.v2/ --name ShapeNetV2 --split examples/splits/sv2_sofas_test.json --surface --skip
# reconstruct meshes from the sofa test split (after 2000 epochs)
python reconstruct.py -e examples/sofas -c 2000 --split examples/splits/sv2_sofas_test.json -d data --skip
# evaluate the reconstructions
python evaluate.py -e examples/sofas -c 2000 -d data -s examples/splits/sv2_sofas_test.json
Team
Jeong Joon Park, Peter Florence, Julian Straub, Richard Newcombe, Steven Lovegrove
Acknowledgements
We want to acknowledge the help of Tanner Schmidt with releasing the code.
License
DeepSDF is relased under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for more details.