GndNet: Fast Ground plane Estimation and Point Cloud Segmentation for Autonomous Vehicles.
Authors: Anshul Paigwar, Ozgur Erkent, David Sierra Gonzalez, Christian Laugier
Introduction
This repository is code release for our GndNet paper accepted in International conference on Robotic Systems, IROS 2020. Link
Abstract
Ground plane estimation and ground point seg-mentation is a crucial precursor for many applications in robotics and intelligent vehicles like navigable space detection and occupancy grid generation, 3D object detection, point cloud matching for localization and registration for mapping. In this paper, we present GndNet, a novel end-to-end approach that estimates the ground plane elevation information in a grid-based representation and segments the ground points simultaneously in real-time. GndNet uses PointNet and Pillar Feature Encoding network to extract features and regresses ground height for each cell of the grid. We augment the SemanticKITTI dataset to train our network. We demonstrate qualitative and quantitative evaluation of our results for ground elevation estimation and semantic segmentation of point cloud. GndNet establishes a new state-of-the-art, achieves a run-time of 55Hz for ground plane estimation and ground point segmentation. 
Installation
We have tested the algorithm on the system with Ubuntu 18.04, 12 GB RAM and NVIDIA GTX-1080.
Dependencies
Python 3.6
CUDA (tested on 10.1)
PyTorch (tested on 1.4)
scipy
ipdb
argparse
numba
Visualization
For visualisation of the ground estimation, semantic segmentation of pointcloud, and easy integration with our real system we use Robot Operating System (ROS):
ROS
ros_numpy
Data Preparation
We train our model using the augmented SematicKITTI dataset. A sample data is provided in this repository, while the full dataset can be downloaded from link. We use the following procedure to generate our dataset:
- We first crop the point cloud within the range of (x, y) = [(-50, -50), (50, 50)] and apply incremental rotation [-10, 10] degrees about the X and Y axis to generate data with varying slopes and uphills. (SemanticKITTI dataset is recorded with mostly flat terrain)
- Augmented point cloud is stored as a NumPy file in the folder reduced_velo.
- To generate ground elevation labels we then use the CRF-based surface fitting method as described in [1].
- We subdivide object classes in SematicKITTI dataset into two categories
- Ground (road, sidewalk, parking, other-ground, vegetation, terrain)
- Non-ground (all other)
- We filter out non-ground points from reduced_velo and use CRF-method [1] only with the ground points to generate an elevation map.
- Our ground elevation is represented as a 2D grid with cell resolution 1m x 1m and of size (x, y) = [(-50, -50), (50, 50)], where values of each cell represent the local ground elevation.
- Ground elevation map is stored as NumPy file in gnd_labels folder.
- Finally, GndNet uses gnd_labels and reduced_velo (consisting of both ground and non-ground points) for training.
If you find the dataset useful consider citing our work and for queries regarding the dataset please contact the authors.
Training
To train the model update the data directory path in the config file: config_kittiSem.yaml
python main.py -s
It takes around 6 hours for the network to converge and model parameters would be stored in checkpoint.pth.tar file. A pre-trained model is provided in the trained_models folder it can be used to evaluate a sequence in the SemanticKITTI dataset.
python evaluate_SemanticKITTI.py --resume checkpoint.pth.tar --data_dir /home/.../kitti_semantic/dataset/sequences/07/
Using pre-trained model
Download the SemanticKITTI dataset from their website link. To visualize the output we use ROS and rviz. The predicted class (ground or non-ground) of the points in the point cloud is substituted in the intensity field of sensor_msgs.pointcloud. In the rviz use intensity as a color transformer to visualize segmented pointcloud. For the visualization of ground elevation, we use the ROS line marker.
roscore
rviz
python evaluate_SemanticKITTI.py --resume trained_models/checkpoint.pth.tar -v -gnd --data_dir /home/.../SemanticKITTI/dataset/sequences/00/
Note: The current version of the code for visualization is written in python which can be very slow specifically the generation of ROS marker. To only visualize segmentation output without ground elevation remove the -gnd flag.
Results
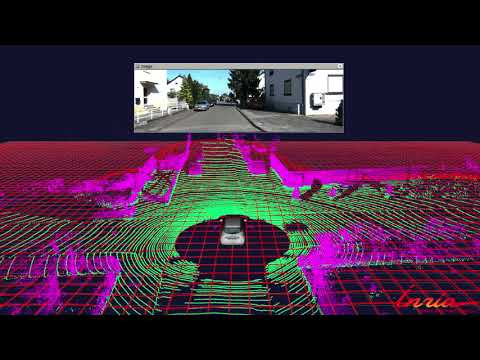
Semantic segmentation of point cloud ground (green) and non-ground (purple):
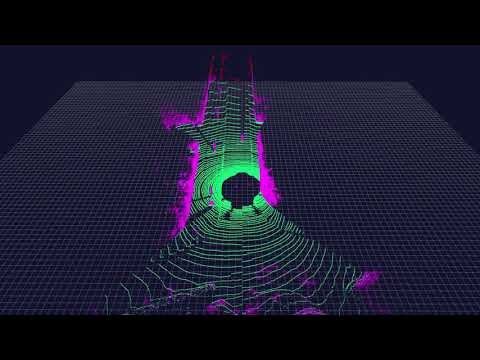
Ground elevation estimation:
YouTube video (Segmentation):
YouTube video (Ground Estimation):
TODO
- Current dataloader loads the entire dataset into RAM first, this reduces training time but it can be hog systems with low RAM.
- Speed up visualization of ground elevation. Write C++ code for ROS marker.
- Create generalized ground elevation dataset to be with correspondence to SemanticKitti to be made public.
Citation
If you find this project useful in your research, please consider citing our work:
@inproceedings{paigwar2020gndnet,
title={GndNet: Fast Ground Plane Estimation and Point Cloud Segmentation for Autonomous Vehicles},
author={Paigwar, Anshul and Erkent, {\"O}zg{\"u}r and Gonz{\'a}lez, David Sierra and Laugier, Christian},
booktitle={IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
year={2020}
}
Contribution
We welcome you for contributing to this repo, and feel free to contact us for any potential bugs and issues.
References
[1] L. Rummelhard, A. Paigwar, A. Nègre and C. Laugier, "Ground estimation and point cloud segmentation using SpatioTemporal Conditional Random Field," 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, 2017, pp. 1105-1110, doi: 10.1109/IVS.2017.7995861.
[2] Behley, J., Garbade, M., Milioto, A., Quenzel, J., Behnke, S., Stachniss, C., & Gall, J. (2019). SemanticKITTI: A dataset for semantic scene understanding of lidar sequences. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 9297-9307).