Rotate-Yolov5
This repository is based on Ultralytics/yolov5, with adjustments to enable rotate prediction boxes.
Section I. Description
The codes are based on Ultralytics/yolov5, and several functions are added and modified to enable rotate prediction boxes.
The modifications compared with Ultralytics/yolov5 and their brief descriptions are summarized below:
-
data/rotate_ucas.yaml : Exemplar UCAS-AOD dataset to test the effects of rotate boxes
-
data/images/UCAS-AOD : For the inference of rotate-yolov5s-ucas.pt
-
models/common.py :
3.1. class Rotate_NMS : Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) module for Rotate Boxes
3.2. class Rotate_AutoShape : Rotate Version of Original AutoShape, input-robust polygon model wrapper for passing cv2/np/PIL/torch inputs. Includes preprocessing, inference and Rotate_NMS
3.3. class Rotate_Detections : Rotate detections class for Rotate-YOLOv5 inference results -
models/rotate_yolov5s_ucas.yaml : Configuration file of rotate yolov5s for exemplar UCAS-AOD dataset
-
models/yolo.py :
5.1. class Rotate_Detect : Detect head for rotate-yolov5 models with rotate box prediction
5.2. class Rotate_Model : Rotate yolov5 models with rotate box prediction -
utils/iou_cuda : CUDA extension for iou computation of polygon boxes
6.1. extensions.cpp : CUDA extension file
6.2. inter_union_cuda.cu : CUDA code for computing iou of polygon boxes
6.3. setup.py : for building CUDA extensions module polygon_inter_union_cuda, with two functions polygon_inter_union_cuda and polygon_b_inter_union_cuda -
utils/autoanchor.py :
7.1. def rotate_check_anchors : Rotate version of original check_anchors
7.2. def rotate_kmean_anchors : Create kmeans-evolved anchors from rotate-enabled training dataset -
utils/datasets.py :
8.1. def polygon_random_perspective : Data augmentation for datasets with polygon boxes (augmentation effects: HSV-Hue, HSV-Saturation, HSV-Value, rotation, translation, scale, shear, perspective, flip up-down, flip left-right, mosaic, mixup)
8.2. def polygon_box_candidates : Polygon version of original box_candidates
8.3. def rotate_random_perspective : Data augmentation for datasets with rotate boxes (augmentation effects: HSV-Hue, HSV-Saturation, HSV-Value, rotation, translation, scale, shear, perspective, flip up-down, flip left-right, mosaic, mixup)
8.4. class Rotate_LoadImagesAndLabels : Rotate version of original LoadImagesAndLabels
8.5. def rotate_load_mosaic : Loads images in a 4-mosaic, with rotate boxes
8.6. def rotate_load_mosaic9 : Loads images in a 9-mosaic, with rotate boxes
8.7. def rotate_verify_image_label : Verify one image-label pair for rotate datasets
8.8. def create_dataloader : Has been modified to include rotate datasets
8.9. class Albumentations : For albumentation augmentation -
utils/general.py :
9.1. def xyxyxyxyn2xyxyxyxy : Convert normalized xyxyxyxy or segments into pixel xyxyxyxy or segments
9.2. def polygon_segment2box : Convert 1 segment label to 1 polygon box label
9.3. def polygon_inter_union_cpu : iou computation (polygon) with cpu
9.4. def polygon_box_iou : Compute iou of polygon boxes via cpu or cuda
9.5. def polygon_b_inter_union_cpu : iou computation (polygon) with cpu
9.6. def polygon_bbox_iou : Compute iou of polygon boxes via cpu or cuda
9.7. def polygon_nms_kernel : Non maximum suppression kernel for polygon-enabled boxes
9.8. def order_corners : Return sorted corners
9.9. def xywhrm2xyxyxyxy : Convert rotate xywhrm into xyxyxyxy, suitable for both pixel-level or normalized
9.10. def xyxyxyxy2xywhrm : Convert xyxyxyxy into rotate xywhrm, suitable for both pixel-level and normalized
9.11. def xywhn2xywh : Convert normalized xywh into pixel xywh
9.12. def rotate_segments2boxes : Convert segment labels to rotate box labels, i.e. (xy1, xy2, ...) to rotated boxes (x, y, w, h, re, im)
9.13. def rotate_scale_coords : Rescale coords (x, y, w, h, re, im) from img1_shape to img0_shape
9.14. def rotate_box_iou : Compute iou of rotate boxes via cpu or cuda
9.15. def rotate_bbox_iou : Compute iou of rotated boxes for class Rotate_ComputeLoss in loss.py via cpu or cuda
9.16. def rotate_non_max_suppression : Runs Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) on inference results for rotated boxes -
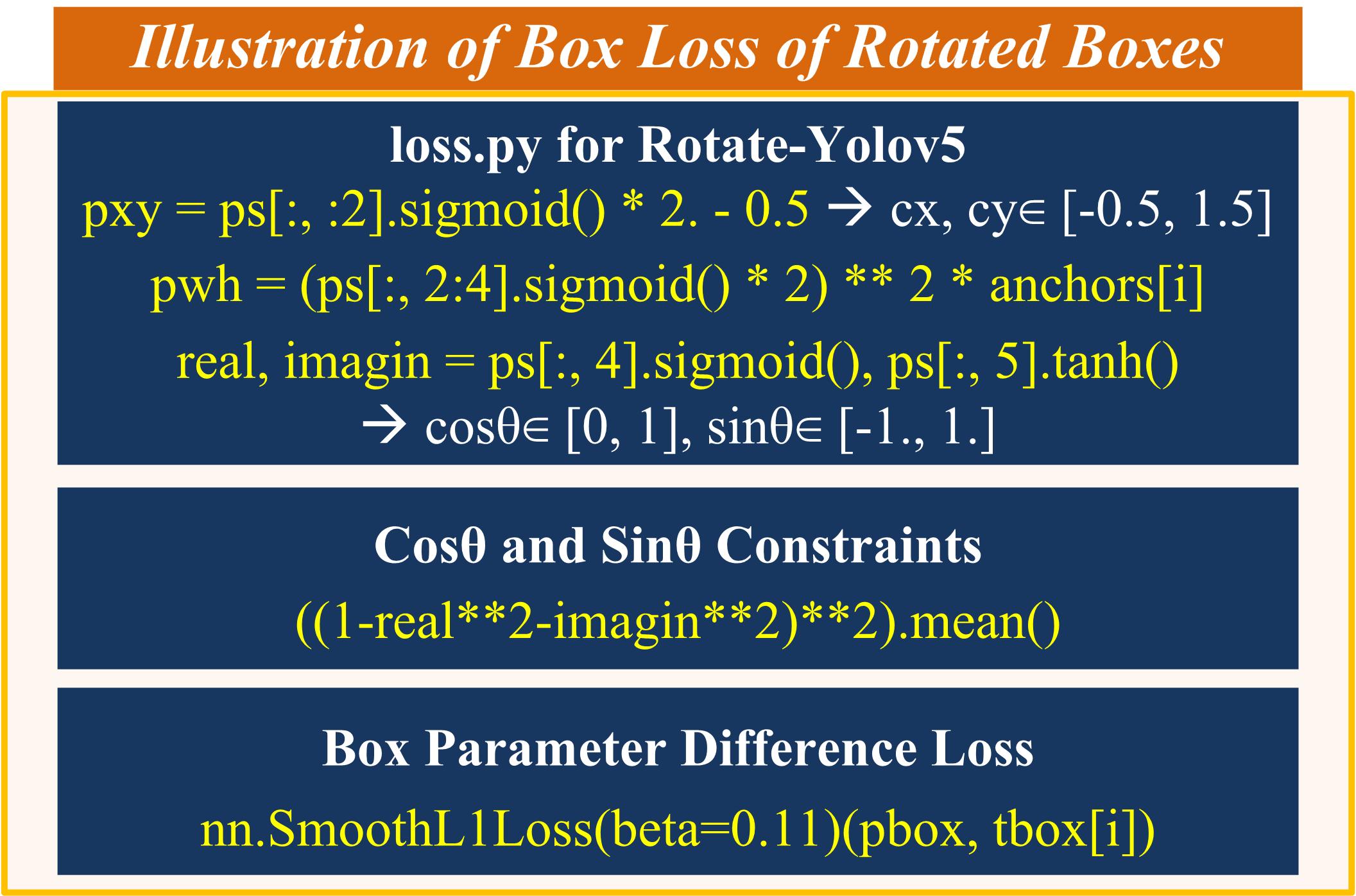
utils/loss.py :
10.1. class Rotate_ComputeLoss : Compute loss for rotate boxes -
utils/metrics.py :
11.1. class Rotate_ConfusionMatrix : Rotate version of original ConfusionMatrix -
utils/plots.py :
12.1. def polygon_plot_one_box : Plot one polygon box on image
12.2. def polygon_plot_one_box_PIL : Plot one polygon box on image via PIL
12.3. def polygon_plot_images : Polygon version of original plot_images
12.4. def rotate_plot_one_box : Plot one rotate box on image
12.5. def rotate_plot_one_box_PIL : Plot one rotate box on image via PIL
12.6. def rotate_output_to_target : Convert model output format [x, y, w, h, re, im, conf, class_id] to target format [batch_id, class_id, x, y, w, h, re, im, conf]
12.7. def rotate_plot_images : Rotate version of original plot_images
12.8. def rotate_plot_test_txt : Rotate version of original plot_test_txt
12.9. def rotate_plot_targets_txt : Rotate version of original plot_targets_txt
12.10. def rotate_plot_labels : Rotate version of original plot_labels -
rotate_train.py : For training rotate-yolov5 models
-
rotate_test.py : For testing rotate-yolov5 models
-
rotate_detect.py : For detecting rotate-yolov5 models
-
requirements.py : Added python model shapely
Section II. How Does Rotate Boxes Work? How Does Rotate Boxes Different from Polygon Boxes?
- Comparisons between Rotate-Yolov5 and Polygon-Yolov5
2. Model Head of Rotate-Yolov5
3. Illustration of Box Loss of Rotated Boxes
Section III. Installation
For the CUDA extension to be successfully built without error, please use CUDA version >= 11.2. The codes have been verified in Ubuntu 16.04 with Tesla K80 GPU.
# The following codes install CUDA 11.2 from scratch on Ubuntu 16.04, if you have installed it, please ignore # If you are using other versions of systems, please check https://tutorialforlinux.com/2019/12/01/how-to-add-cuda-repository-for-ubuntu-based-oses-2/ # Install Ubuntu kernel head sudo apt install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
# Pinning CUDA repo wget https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1604/x86_64/cuda-ubuntu1604.pin sudo mv cuda-ubuntu1604.pin /etc/apt/preferences.d/cuda-repository-pin-600
# Add CUDA GPG key sudo apt-key adv --fetch-keys http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1604/x86_64/7fa2af80.pub
# Setting up CUDA repo sudo add-apt-repository "deb https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu1604/x86_64/ /"
# Refresh apt repositories sudo apt update
# Installing CUDA 11.2 sudo apt install cuda-11-2 -y sudo apt install cuda-toolkit-11-2 -y
# Setting up path echo 'export PATH=/usr/local/cuda-11.2/bin${PATH:+:${PATH}}' >> $HOME/.bashrc # You are done installing CUDA 11.2
# Check NVIDIA nvidia-smi # Update all apts sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get -y upgrade
# Begin installing python 3.7 curl -o ~/miniconda.sh -O https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.sh chmod +x ~/miniconda.sh ./miniconda.sh -b echo "PATH=~/miniconda3/bin:$PATH" >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc conda install -y python=3.7 # You are done installing python
The following codes set you up with the Rotate Yolov5.
# clone git repo git clone https://github.com/XinzeLee/RotateObjectDetection cd RotateObjectDetection/rotate-yolov5 # install python package requirements pip install -r requirements.txt # install CUDA extensions cd utils/iou_cuda python setup.py install # cd back to rotate-yolov5 folder cd .. && cd ..
Section IV. Rotate-Tutorial 1: Deploy the Rotate Yolov5s
Try Rotate Yolov5s Model by Following Rotate-Tutorial 1
- Inference
- Test
- Train
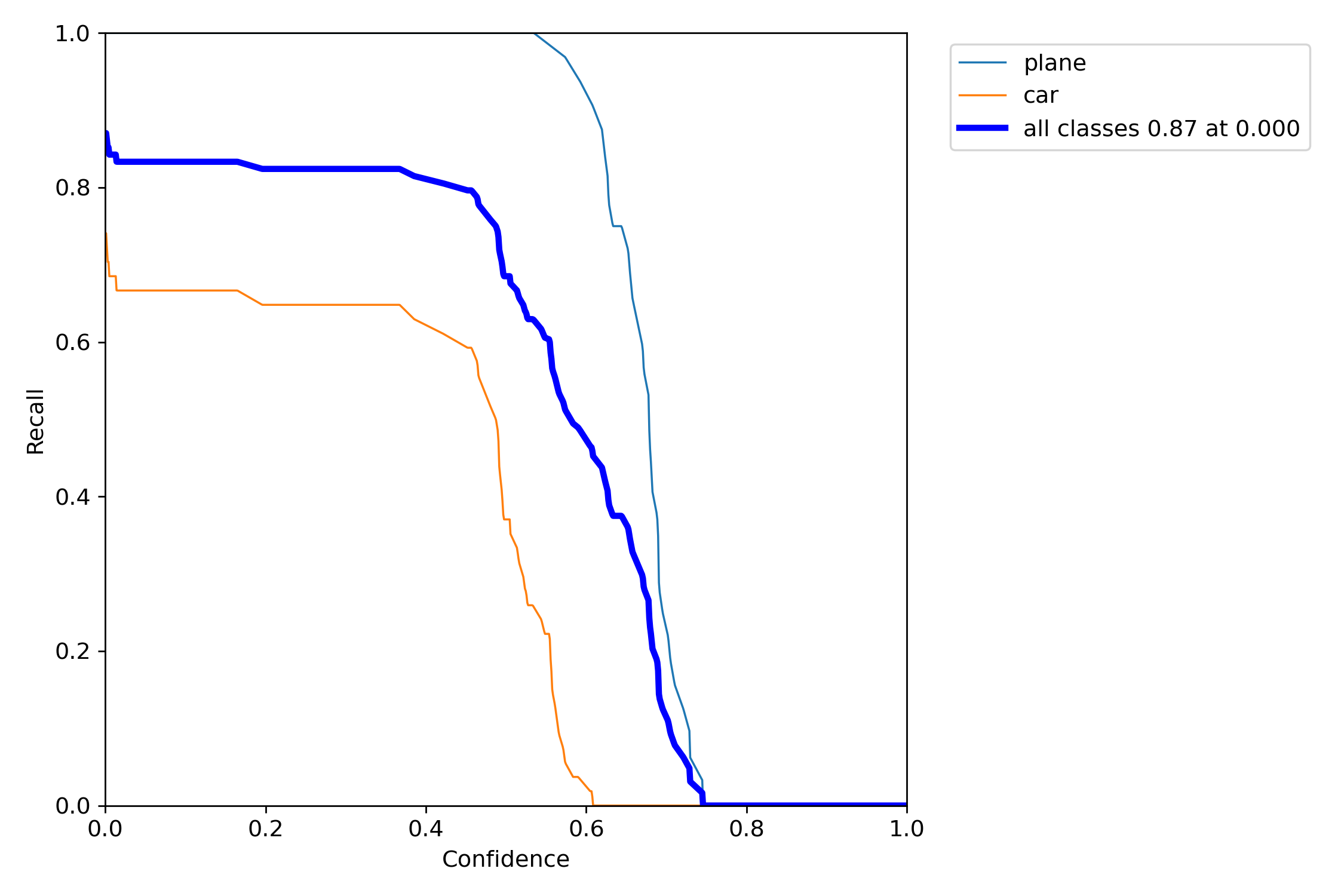
$ python rotate_train.py --weights rotate-yolov5s-ucas.pt --cfg rotate_yolov5s_ucas.yaml \ --data rotate_ucas.yaml --hyp hyp.ucas.yaml --img-size 1024 \ --epochs 3 --batch-size 12 --noautoanchor --rotate --cache - Performance
Section V. Rotate-Tutorial 2: Transform COCO Dataset to Rotate Labels Using Segmentation
Transform COCO Dataset to Rotate Labels by Following Rotate-Tutorial 2