Grounded Situation Recognition with Transformers
- This is the official PyTorch implementation of Grounded Situation Recognition with Transformers (BMVC 2021).
- GSRTR (Grounded Situation Recognition TRansformer) achieves state of the art in all evaluation metrics on the SWiG benchmark.
- This repository contains instructions, code and model checkpoint.
Overview
Grounded Situation Recognition (GSR) is the task that not only classifies a salient action (verb), but also predicts entities (nouns) associated with semantic roles and their locations in the given image. Inspired by the remarkable success of Transformers in vision tasks, we propose a GSR model based on a Transformer encoder-decoder architecture. The attention mechanism of our model enables accurate verb classification by capturing high-level semantic feature of an image effectively, and allows the model to flexibly deal with the complicated and image-dependent relations between entities for improved noun classification and localization. Our model is the first Transformer architecture for GSR, and achieves the state of the art in every evaluation metric on the SWiG benchmark.
GSRTR mainly consists of two components: Transformer Encoder for verb prediction, and Transformer Decoder for grounded noun prediction. For details, please see Grounded Situation Recognition with Transformers by Junhyeong Cho, Youngseok Yoon, Hyeonjun Lee and Suha Kwak.
Environment Setup
We provide instructions for environment setup.
# Clone this repository and navigate into the repository
git clone https://github.com/jhcho99/gsrtr.git
cd gsrtr
# Create a conda environment, activate the environment and install PyTorch via conda
conda create --name gsrtr python=3.9
conda activate gsrtr
conda install pytorch==1.8.0 torchvision==0.9.0 cudatoolkit=11.1 -c pytorch -c conda-forge
# Install requirements via pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
SWiG Dataset
Annotations are given in JSON format, and annotation files are under "SWiG/SWiG_jsons/" directory. Images can be downloaded here. Please download the images and store them in "SWiG/images_512/" directory.
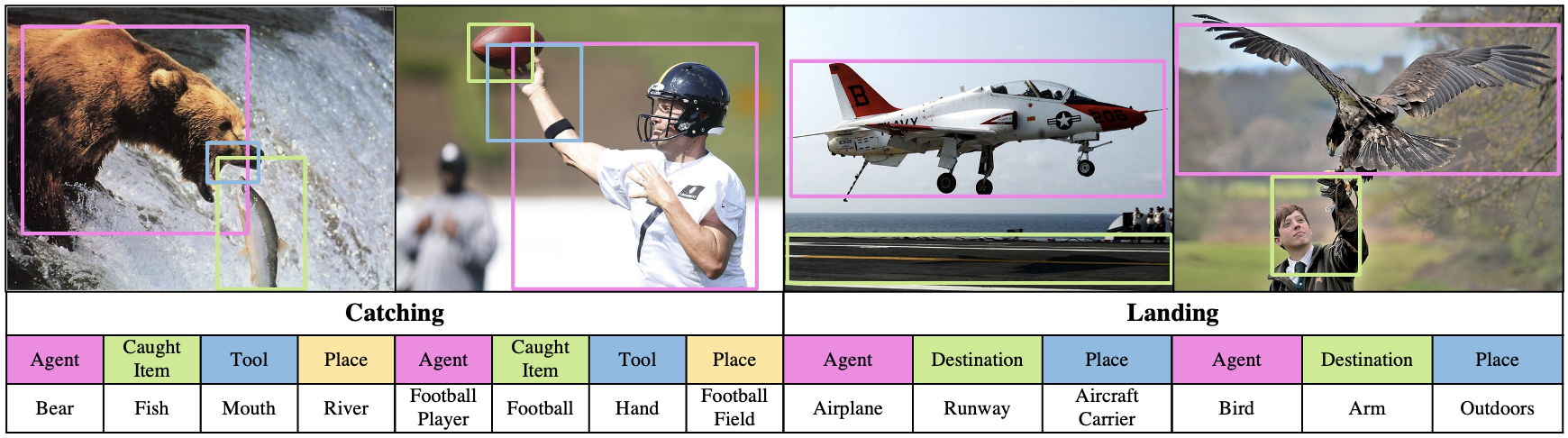 In the SWiG dataset, each image is associated with Verb, Frame and Groundings.
In the SWiG dataset, each image is associated with Verb, Frame and Groundings.
A) Verb: each image is paired with a verb. In the annotation file, "verb" denotes the salient action for an image.
B) Frame: a frame denotes the set of semantic roles for a verb. For example, the frame for verb "Catching" denotes the set of semantic roles "Agent", "Caught Item", "Tool" and "Place". In the annotation file, "frames" show the set of semantic roles for a verb, and noun annotations for each role. There are three noun annotations for each role, which are given by three different annotators.
C) Groundings: each grounding is described in [x1, y1, x2, y2] format. In the annotation file, "bb" denotes groundings for roles. Note that nouns can be labeled without groundings, e.g., in the case of occluded objects. When there is no grounding for a role, [-1, -1, -1, -1] is given.
# an example of annotation for an image
"catching_175.jpg": {
"verb": "catching",
"height": 512,
"width": 910,
"bb": {"tool": [-1, -1, -1, -1],
"caughtitem": [444, 169, 671, 317],
"place": [-1, -1, -1, -1],
"agent": [270, 112, 909, 389]},
"frames": [{"tool": "n05282433", "caughtitem": "n02190166", "place": "n03991062", "agent": "n00017222"},
{"tool": "n05302499", "caughtitem": "n02190166", "place": "n03990474", "agent": "n00017222"},
{"tool": "n07655505", "caughtitem": "n13152742", "place": "n00017222", "agent": "n02190166"}]
}
In imsitu_space.json file, there is additional information for verb and noun.
# an example of additional verb information
"catching": {
"framenet": "Getting",
"abstract": "an AGENT catches a CAUGHTITEM with a TOOL at a PLACE",
"def": "capture a sought out item",
"order": ["agent", "caughtitem", "tool", "place"],
"roles": {"tool": {"framenet": "manner", "def": "The object used to do the catch action"},
"caughtitem": {"framenet": "theme", "def": "The entity being caught"},
"place": {"framenet": "place", "def": "The location where the catch event is happening"},
"agent": {"framenet": "recipient", "def": "The entity doing the catch action"}}
}
# an example of additional noun information
"n00017222": {
"gloss": ["plant", "flora", "plant life"],
"def": "(botany) a living organism lacking the power of locomotion"
}
Additional Details
- All images should be under "SWiG/images_512/" directory.
- train.json file is for train set.
- dev.json file is for development set.
- test.json file is for test set.
Training
To train GSRTR on a single node with 4 gpus for 40 epochs, run:
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=4 --use_env main.py \
--backbone resnet50 --batch_size 16 --dataset_file swig --epochs 40 \
--num_workers 4 --enc_layers 6 --dec_layers 6 --dropout 0.15 --hidden_dim 512 \
--output_dir gsrtr
To train GSRTR on a Slurm cluster with submitit using 4 TITAN Xp gpus for 40 epochs, run:
python run_with_submitit.py --ngpus 4 --nodes 1 --job_dir gsrtr \
--backbone resnet50 --batch_size 16 --dataset_file swig --epochs 40 \
--num_workers 4 --enc_layers 6 --dec_layers 6 --dropout 0.15 --hidden_dim 512 \
--partition titanxp
- A single epoch takes about 30 minutes. 40 epoch training takes around 20 hours on a single machine with 4 TITAN Xp gpus.
- We use AdamW optimizer with learning rate 10-4 (10-5 for backbone), weight decay 10-4 and β = (0.9, 0.999).
- Random Color Jittering, Random Gray Scaling, Random Scaling and Random Horizontal Flipping are used for augmentation.
Inference
To run an inference on a custom image, run:
python inference.py --image_path inference/filename.jpg \
--saved_model gsrtr_checkpoint.pth \
--output_dir inference
- Model checkpoint can be downloaded here.
Here is an example of inference result: 
Acknowledgements
Our code is modified and adapted from these amazing repositories:
Contact
Junhyeong Cho ([email protected])
Citation
If you find our work useful for your research, please cite our paper:
@InProceedings{cho2021gsrtr,
title={Grounded Situation Recognition with Transformers},
author={Junhyeong Cho and Youngseok Yoon and Hyeonjun Lee and Suha Kwak},
booktitle={British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC)},
year={2021}
}
License
GSRTR is released under the Apache 2.0 license. Please see the LICENSE file for more information.
